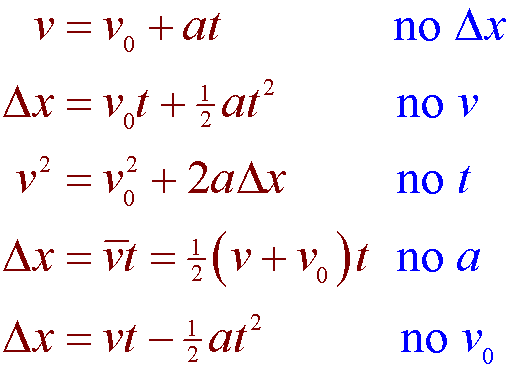Beautiful Work Distance Acceleration Formula

2Now we have expressed the distance traveled as a function of final instantaneous speed and time.
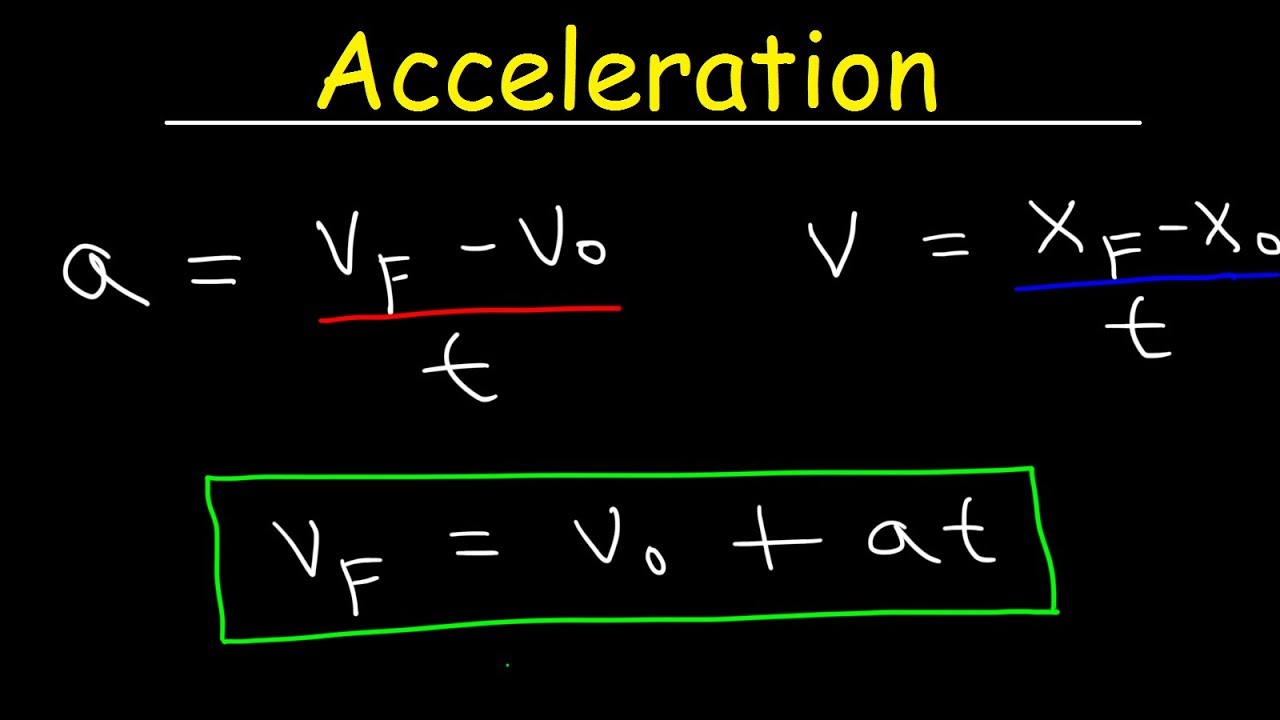
Distance acceleration formula. D vt 12at2 where d is distance traveled in a certain amount of time t v is starting velocity a is acceleration must be constant and t is time. Your acceleration is 266 meters per second 2 and your final speed is 1463 meters per second. Calculating distance from acceleration is as easy as using this formula.
Example 4 A particle starts from rest with an acceleration at which varies according to the equation at cos πt 6 m s2. D vt 12at2. You need to subtract the initial velocity from the final velocity.
Find the distance traveled by the particle for the 3rd second. 3 to s 0 ms 333 ms 5 s 2 833 m The acceleration can be calculated with eq. Dividing distance by time twice is the same as dividing distance by the square of time.
T f is the final time and t i is the initial time. A common application for this equation is the travel associated with the free fall of an object under the force of gravity. It tells about how far an object moves in a given interval of time.
Velocity acceleration and distance This equation applies to objects in uniform acceleration. Thus the SI unit of acceleration is the meter per second squared. Final velocity2 initial velocity2 2 acceleration distance v 2 u 2 2αx.
6by time t we get vf. This gives you the distance traveled during a certain amount of time. In the case of Earths gravity the constant acceleration is approximately 980665 ms 2.