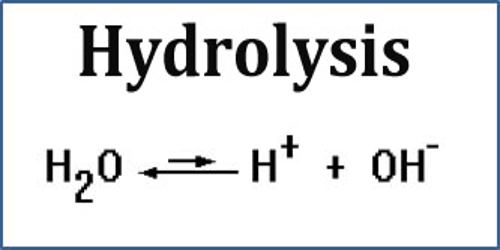Smart Hydrolysis Reaction Equation
The molecular and net ionic equations are shown below.
Hydrolysis reaction equation. The term comes from the Greek prefix hydro - water and lysis to break apart. General formula of a hydrolysis reaction is. Therefore the overall hydrolysis kinetics has three contributing components.
While it may seem that salt solutions would always be neutral they can frequently be either acidic or basic. Consider the salt formed when the weak acid hydrofluoric acid is neutralized by the strong base sodium hydroxide. Definition Reaction Equation Example Instructor.
Again one of the phosphate groups undergoes hydrolysis to form the acid and a phosphate ion giving off energy. The enzyme-catalyzed reactions of Phase I metabolism bind oxygen hydrogen water or amino acids to the lipophilic drug molecule to expose or introduce a hydroxyl -OH amino -NH 2 sulfhydryl -SH or carboxyl -COOH polar functional group and thus result in a modest increase in the parent drugs water solubilityThese reactions include hydrolysis reduction and oxidation. Rate of hydrolysis kh RX where kh kAH kN kBOH-.
Hydrolysis refers to the reaction of a substance with water or its ions. A Ray Tatum Show bio A. 21212 HF a q NaOH a q NaF a q H 2 O l 21213 HF a q OH a q F a q H 2 O l.
This is the final reaction in glycolysis. Hydrolysis in chemistry and physiology a double decomposition reaction with water as one of the reactants. Acid hydrolysis is a reaction with acidified water acidic conditions.
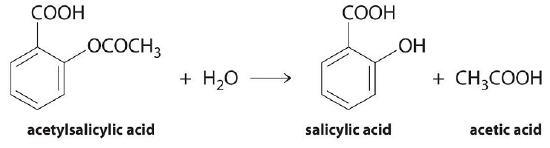
In a hydrolysis reaction involving an ester link such as that found between two amino acids in a protein the molecule is split. Disaccharides can be hydrolysed under acidic conditions. Hydrolysis reactions are generally enhanced by both acids and bases and three independent reaction mechanisms account for neutral acid and base hydrolysis.