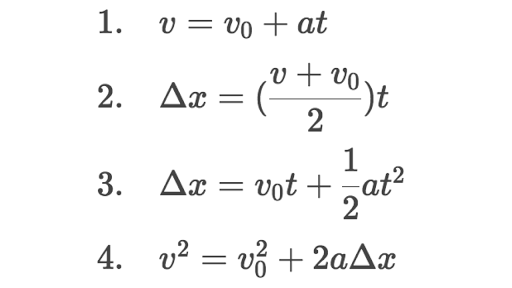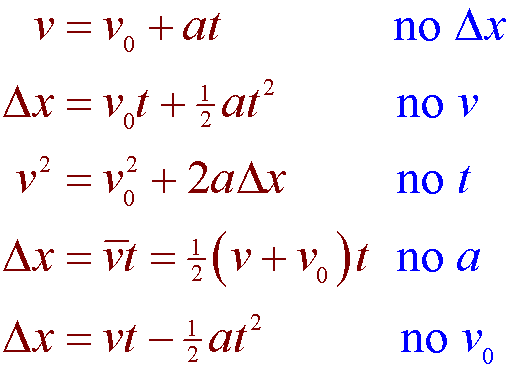Supreme 2 Dimensional Motion Equations

Where and.
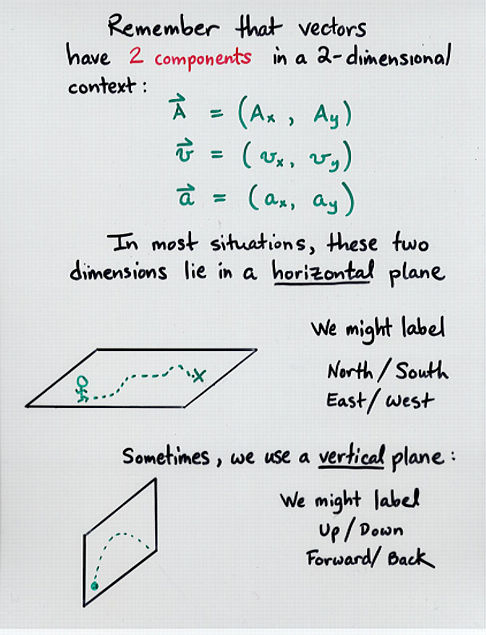
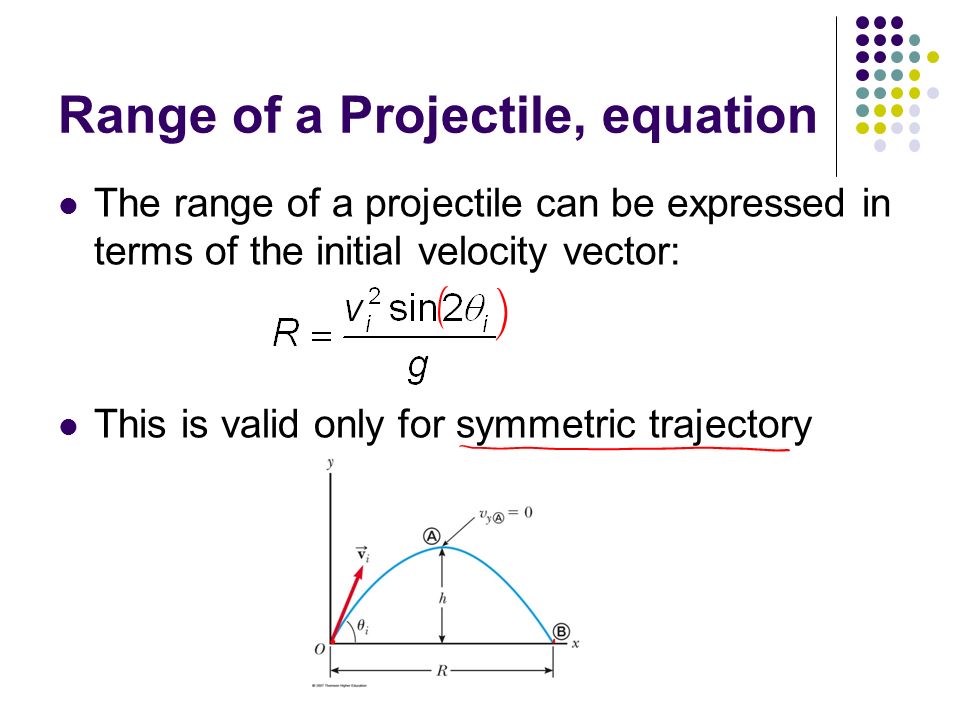
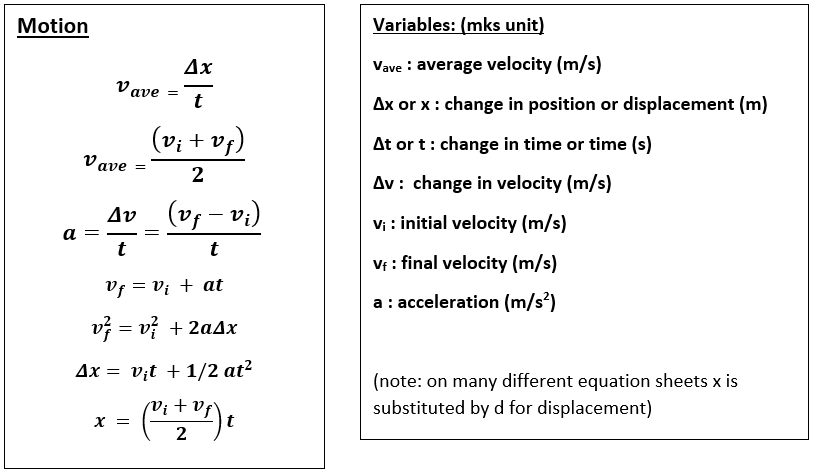
2 dimensional motion equations. Motion in two dimensions opens up infinite possibilities of directions since positions can be anywhere in the x-y plane ie any combination of x and y defines a position. Equations of Kinematics in Two Dimensions. T 2 Vy g Range of the projectile.
This idea is central to the field of analytical geometry. Lets sum that up to form the most essential projectile motion equations. When considering three dimensional bodies undergoing two dimensional motion the moment of inertia needsRm to be defined with respect to an axis perpendicular to the plane of motion.
One thing to notice is that the time t is the only thing that doesnt involve an x or a y. Since the vertical acceleration is constant we can solve for a vertical variable with one of the four kinematic formulas which are shown below. 8 rows Motion in two dimensions can be thoroughly described with two independent one-dimensional equations.
We also show how this inequality of Korns type has been recently extended to surfaces with little regularity Thm. According to Newtons second law the equation of motion of the particle is. Lets escape from the binds of one-dimension where we were forced to launch things straight up and start launching at angles.
Be sure to only plug vertical variables into these vertical equations. R 2 Vx Vy g. In general we have the following 8 equations 4 per dimension.
To understand how displacement velocity and acceleration are applied to two-dimensional motion consider a spacecraft equipped with. As a result mathematical models of motion in two dimensions are more complicated and vectors have to be used at every level of the motions description. Vx V cosα Vertical velocity component.